By default, FTP Client is available on Windows Computer. You can using FTP Commands on Command Prompt or PowerShell to transfer any data to and from a computer running a File Transfer Protocol Server.
FTP is not an encrypted transmission, which means anyone could read any data sent over it. For secure data transmission, FTP is secured by SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced by SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
FTP Syntax and Parameters
Below is the list of the commands available when you are using Windows command-line FTP Client.
ftp [-v] [-d] [-i] [-n] [-g] [-s:filename] [-a] [-w:windowsize] [computer]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -v | Suppresses display of remote server responses. |
| -d | Enables debugging, displaying all commands passed between the FTP client and FTP server. |
| -i | Disables interactive prompting during multiple file transfers. |
| -n | Suppresses auto-login upon initial connection. |
| -g | Disables file name globbing. Glob permits the use of the asterisk (*) and question mark (?) as wildcard characters in local file and path names. For more information, see additional references. |
| -s: | Specifies a text file that contains ftp commands. These commands run automatically after ftpstarts. This parameter allows no spaces. Use this parameter instead of redirection (<). Note:In Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or later operating systems, the text file must be written in UTF-8. |
| -a | Specifies that any local interface can be used when binding the ftp data connection. |
| -A | Logs onto the ftp server as anonymous. |
| -x: | Overrides the default SO_SNDBUF size of 8192. |
| -r: | Overrides the default SO_RCVBUF size of 8192. |
| -b: | Overrides the default async buffer count of 3. |
| -w: | Specifies the size of the transfer buffer. The default window size is 4096 bytes. |
| -? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
| Specifies the computer name, IP address, or IPv6 address of the ftp server to which to connect. The host name or address, if specified, must be the last parameter on the line. |
There are some information for the FTP commands:
- ftp command-line parameters are case-sensitive
- this command is available only if TCP/IP protocol is installed
- ftp supports IPv6 when the IPv6 protocol installed
Connect using FTP
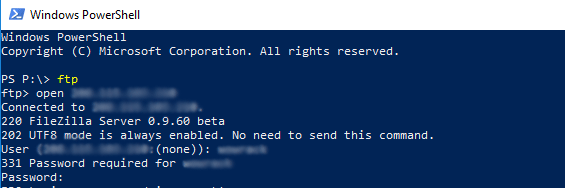
To connect to an FTP Server, you can easily open Command Prompt or PowerShell and type FTP and press enter. Once the
open [ftpserver] [port]
For example, you want to connect to ftp server on server 192.168.1.15 using default port, you can run the command below on your PowerShell or Command Prompt:
open 192.168.1.15
Once the connection to the FTP server established, a username and password prompt will appear.
Example FTP Commands
| FTP Command | Description of Command |
|---|---|
| ! | This command toggles back and forth between the operating system and ftp. Once back in the operating system, typing exit takes you back to the FTP command line. |
| ? | Accesses the Help screen. |
| append | Append text to a local file. |
| ascii | Switch to ASCII transfer mode. |
| bell | Turns bell mode on or off. |
| binary | Switches to binary transfer mode. |
| bye | Exits from FTP. |
| cd | Changes directory. |
| close | Exits from FTP. |
| delete | Deletes a file. |
| debug | Sets debugging on or off. |
| dir | Lists files, if connected. dir -C = lists the files in wide format. dir -1 = Lists the files in bare format in alphabetic order. dir -r = Lists directory in reverse alphabetic order. dir -R = Lists all files in current directory and sub directories. dir -S = Lists files in bare format in alphabetic order. |
| disconnect | Exits from FTP. |
| get | Get file from the remote computer. |
| glob | Sets globbing on or off. When turned off, the file name in the put and get commands is taken literally, and wildcards will not be looked at. |
| hash | Sets hash mark printing on or off. When turned on, for each 1024 bytes of data received, a hash-mark (#) is displayed. |
| help | Accesses the Help screen and displays information about the command if the command is typed after help. |
| lcd | Displays local directory if typed alone or if path typed after lcd will change the local directory. |
| literal | Sends a literal command to the connected computer with an expected one-line response. |
| ls | Lists files of the remotely connected computer. |
| mdelete | Multiple delete. |
| mdir | Lists contents of multiple remote directories. |
| mget | Get multiple files. |
| mkdir | Make directory. |
| mls | Lists contents of multiple remote directories. |
| mput | Send multiple files. |
| open | Opens address. |
| prompt | Enables or disables the prompt. |
| put | Send one file. |
| pwd | Print working directory. |
| quit | Exits from FTP. |
| quote | Same as the literal command. |
| recv | Receive file. |
| remotehelp | Get help from remote server. |
| rename | Renames a file. |
| rmdir | Removes a directory on the remote computer. |
| send | Send single file. |
| status | Shows status of currently enabled and disabled options. |
| trace | Toggles packet tracing. |
| Type | Set file transfer type. |
| user | Send new user information. |
| verbose | Sets verbose on or off. |
Below some examples for the list of the FTP Commands above.
Send and Receive File in FTP
To send a file from your local computer to the remote FTP server after you connected, use the send command. Below the example command to send testfile.txt to the current working directory.
ftp> send testfile.txt
To get a file from the remote FTP server, you can use get command to do it. Below the example command to copy testfile.txt from the current working directory to your local directory.
ftp> get testfile.txt
Terminate FTP Session and Exit
We can terminate the current FTP session and exit from FTP shell with exit command.
ftp> close
Delete Remote File
We can delete the remote file with delete command. Below is the example to delete a file named testfile.txt
ftp> delete testfile.txt